Google Webmaster Tools
What is Google Webmaster Tools?
Google Webmaster Tools - now Google Search Console - is a free tool by Google that allows users to check how their website is performing in the search results and whether it experiences any issues that can affect that performance.
It was launched in June 2005 as Sitemaps, an XML tool. That same year in November, Google began adding non-sitemap features and metrics to Sitemaps, such as query stats, crawl stats and errors, and index stats.
In August 2006, Sitemaps became Google Webmaster Tools. The name change had to better reflect the tool’s goal of helping webmasters get better coverage and visibility on Google.
Over time, it became clear that the user base of Google Webmaster Tools consists of a much broader audience than webmasters alone and so Google rebranded the tool again in May 2015 to Google Search Console.
We still know it under that name today, but the current look and features of the tool largely go back to January 2018, when Google rolled out a revamped version. New functionalities were introduced over the course of several months and the tool graduated out of Beta in September of that same year.
Why is Google Search Console (formerly Webmaster Tools) important?
Google Search Console (GSC) is important because it lets users monitor their sites’ visibility in search, spot crawling issues, and communicate changes and fixes to Google.
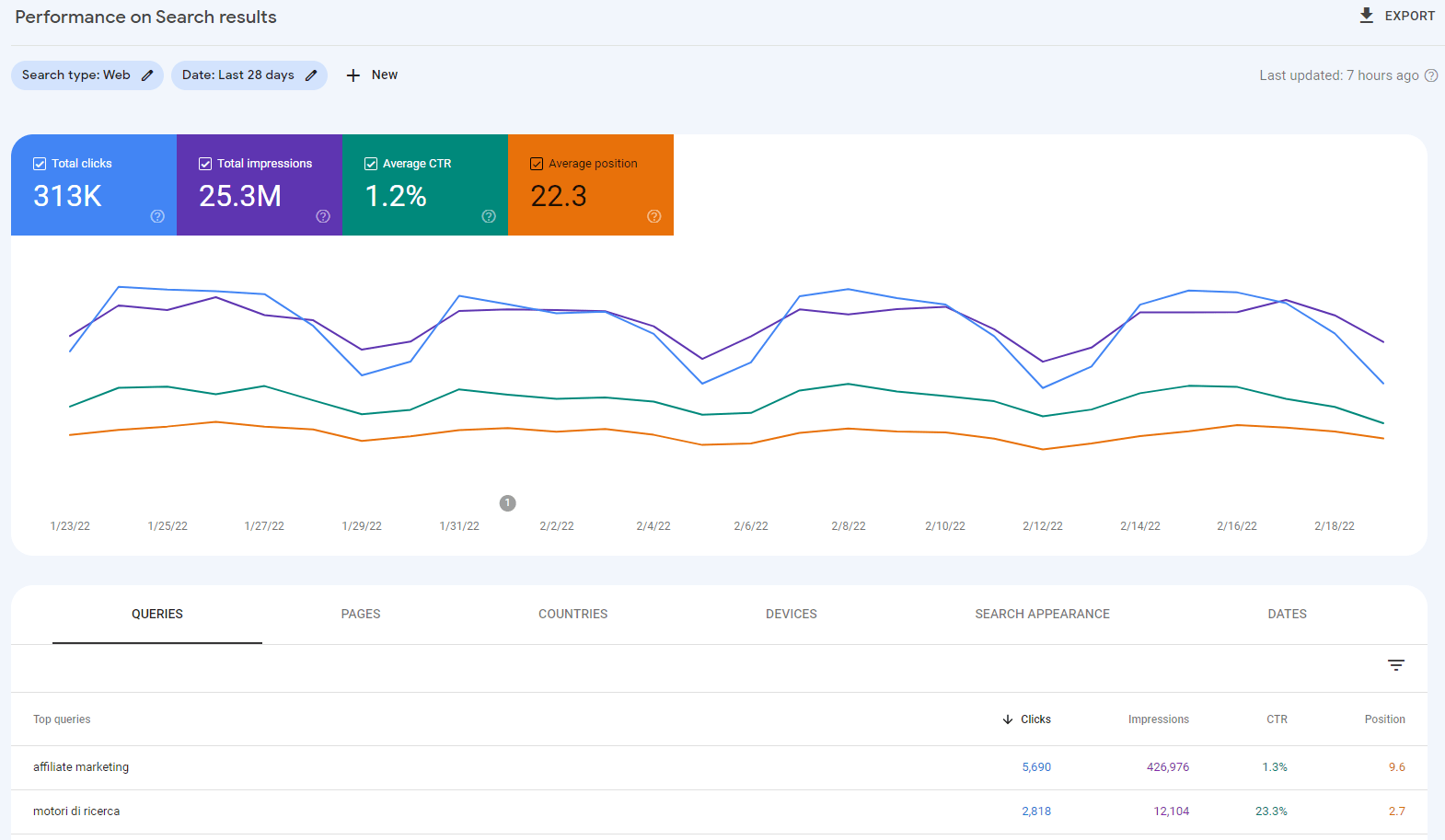
One of GSC’s main functionalities is its Search results Performance report. It shows you which keywords your site ranks for at which positions, and how many impressions and clicks those keywords get in different countries. This report is crucial when you want to improve your rankings.
To make sure Google knows which of your pages should appear in the search results, you can submit sitemaps as well as individual URLs in GSC. The tool will let you know what the current status of your sitemaps is and alert you of any indexing issues.
It also tells you if something on your site is causing mobile usability issues and whether the rich results your site returns are error-free. The Enhancements reports bring up issues with structured data, while the Core Web Vitals report flags pages that are too slow.
If you experience a sudden drop in rankings, you might want to check the Manual Actions report to make sure Google hasn’t deemed your site non-compliant with its quality guidelines.
And if something looks off, you can consult the Security report to see if Google came across any hacked content or malware. Google also raises a security issue when your site is trying to get a user to do something that could be harmful to them, such as reveal confidential information.
Targeting an international audience? Then you can use the International Targeting report in Google Search Console to monitor your hreflang setup. This is also where you can set a site-wide target country.
Another important section of GSC is its Links report, where you can monitor which sites link to yours most, and what your top-linked pages are.
These and other functionalities of Google Search Console make it an indispensable tool for website owners and operators.
Best practices for Google Search Console
1. Use the right property type when adding a website
You can add a website to Google Search Console in two ways: as a URL-prefix property, or as a Domain property.
When you add your website as a URL-prefix, Google Search Console will only track all the URLs that start with this prefix. Adding a URL-prefix such as https://ahrefs.com/blog won’t cover https://ahrefs.com or https://ahrefs.com/blog/.
This makes URL-prefix properties a good option when you want to monitor data separately for multiple subsections of your site. For example:
- https://website.com/blog/
- https://website.com/store/
- https://website.com/france/
If you add a website as a Domain property, it will cover all of the URLs on that domain or subdomain. So if you want to monitor your entire website as one property, the Domain option is the way to go.
2. Monitor the Coverage report regularly
The Coverage report flags crawl errors on your website. You want to fix these as soon as possible as they hurt your search visibility directly.
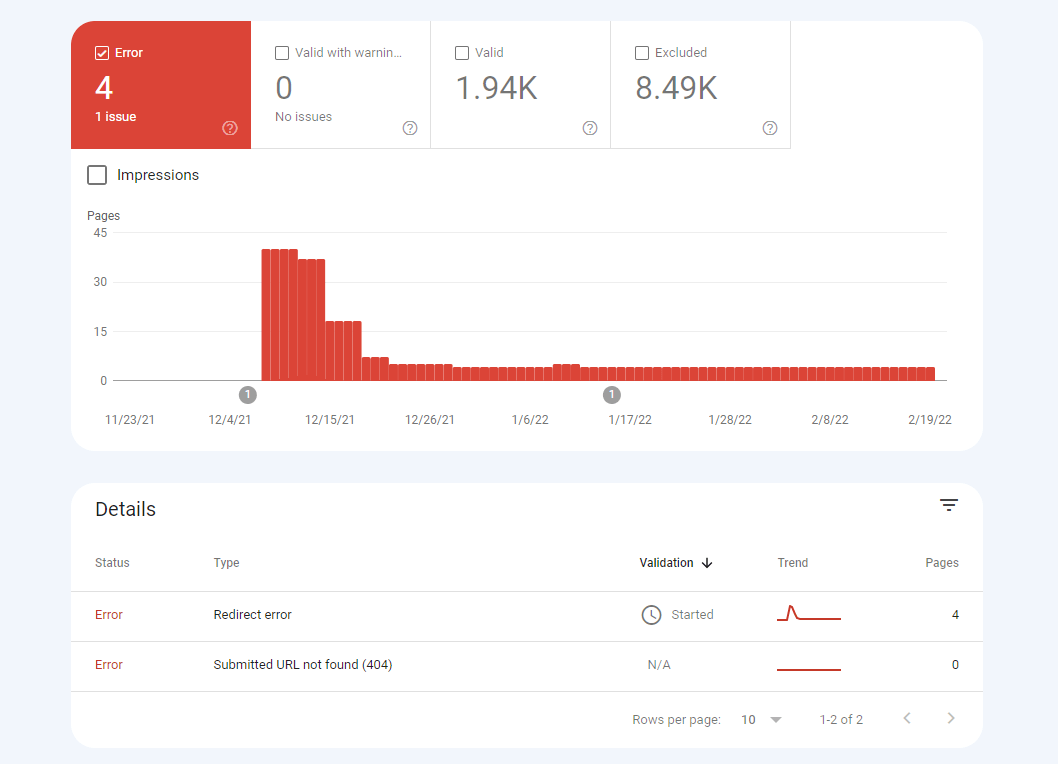
The “Excluded” section of the Coverage report shows you which pages on your site are excluded from being indexed. Check this regularly to verify that none of the pages you want to appear in the search results show up here.
3. Don’t get too obsessed with Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals report is based on three metrics:
- LCP (largest contentful paint)
- FID (first input delay)
- CLS (cumulative layout shit)
While they are a confirmed ranking factor, they’re not crucial and there’s no need to obsess over getting perfect scores. Having quality content, solid backlinks, and strong technical SEO is still more important than optimizing for perfect Core Web Vital scores.
4. Remember that Google Search Console only shows a sample of links
The tables in Google Search Console are limited to 1,000 rows of data and while you can export a larger sample set, it’s still limited to 100,000 links. GSC also doesn’t differentiate between followed and nofollow links. It really just gives you a glimpse of the state of your link profile.
To see the bigger picture, use Ahrefs’ Webmaster Tools. It shows you all known links to your website, flags broken internal and external links, and gives you detailed link type data (nofollow, UGC, sponsored).
FAQs
What’s the difference between Google Analytics and Google Search Console?
Google Analytics provides data on user behavior and focuses on how users enter, interact with, and leave your website, while Google Search Console is search engine-focused and provides data on how your website appears in and is crawled by Google.
Is GSC free?
Yes, Google Search Console is free to use.
Can a website rank well without Google Search Console?
As per Google: “You don’t have to sign up for Search Console to be included in Google Search results, but Search Console helps you understand and improve how Google sees your site.”
Does GSC show all links to a website?
No, all the link reports in Google Search Console are limited to the top 1,000 results, and sample exports are limited to 100,000 links.