Title Tag
What is a Title Tag?
The title tag is an HTML element containing a webpage’s title. The page title appears in Google’s search results, social media feeds, and in the browser tab.
Here’s how it looks in its raw form:
![]()
And here’s how it is displayed
On Facebook:
In the browser tab:
On Google’s SERP:
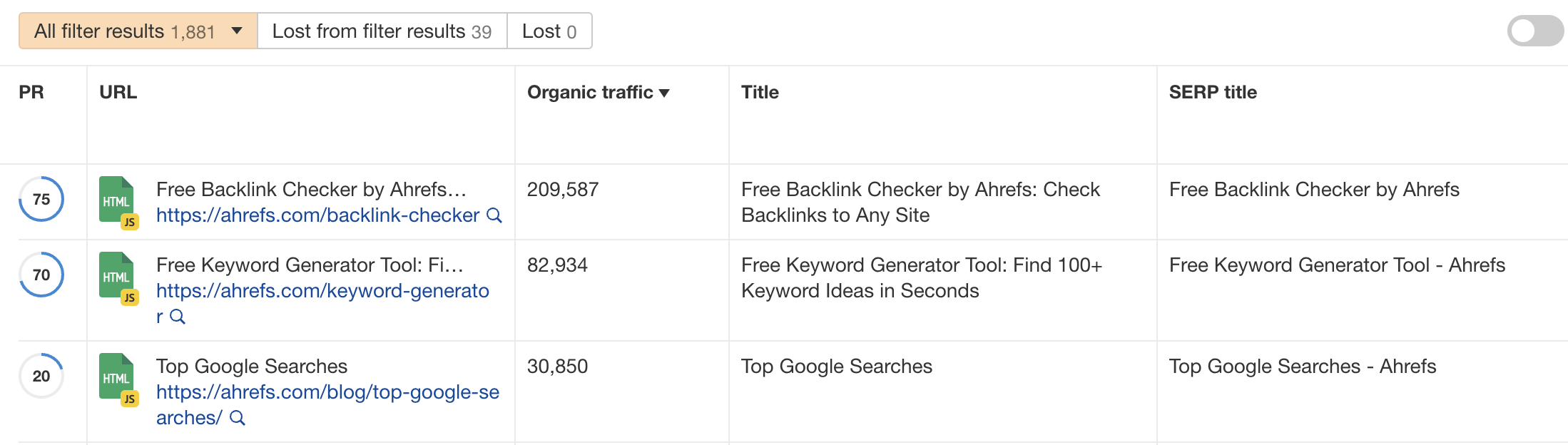
However, you should note that Google does not always use the exact title tag on SERP. According to our study, Google rewrites every 3rd title on SERP.
Here’s an example of Google rewriting page titles for our own website:
Why is the title tag important?
The title tag tells visitors and search engines what they can expect from the web page (in the shortest and most concise way possible). And because page titles are the first thing people see on SERPs and in social media feeds, they influence the click-through rates a lot.
Most often, the title is the first thing a potential visitor will notice when coming across your page. So this is your chance to make a positive first impression.
Besides, Google and other search engines use title tags to understand the pages and tank them. And even if it is a minor ranking factor, it should not be neglected.
SEO best practices for writing page titles
1. Use your primary keyword in the title tag
Keywords connect what searchers are looking for to the information you’re providing. Use a primary keyword you’re targeting in the title tag as it captures the reader’s attention and tells Google your web page is relevant to the searcher’s query.
Furthermore, a visitor will likely click on a webpage with the precise keyword they just typed. It’ll help with click-through rates.

2. Keep it short
Longer titles will be trimmed or replaced on Google’s SERPs. Therefore, keeping your title tag under 50-60 characters is important. Since the pixel width on SERP limits the title length, we’d highly recommend using a title tag preview tool.
3. The title and H1 tags can be different
As we’ve explained above, keeping the page title short is recommended, but it does not mean that the H1 tag must be short, too, or that it must duplicate the title. You can write a shorter title for Google and a bit longer H1 for your readers.
Here’s an example from our blog where the title tag and H1 tags are different:

4. Make your titles unique and engaging
Your goal is to engage the audience before they read the content. And the best way is by making the title tag compelling, easily recognizable, and exclusive.
The title tag should evoke curiosity while refraining from confusing searchers who rely on it to find the information they need.
Most tips about the title tags that you can find online are written by SEOs, but we also recommend you check the recommendations from Google:
Influencing your title links in search results
FAQs
Should the title tag and H1 tag be identical?
You are not obliged to use the same text in the title tag and in H1.
You can write a shorter title for the search engines and social networks and a bit longer H1 that will be the first visible element on the page for your visitors. But you should not make them completely different.
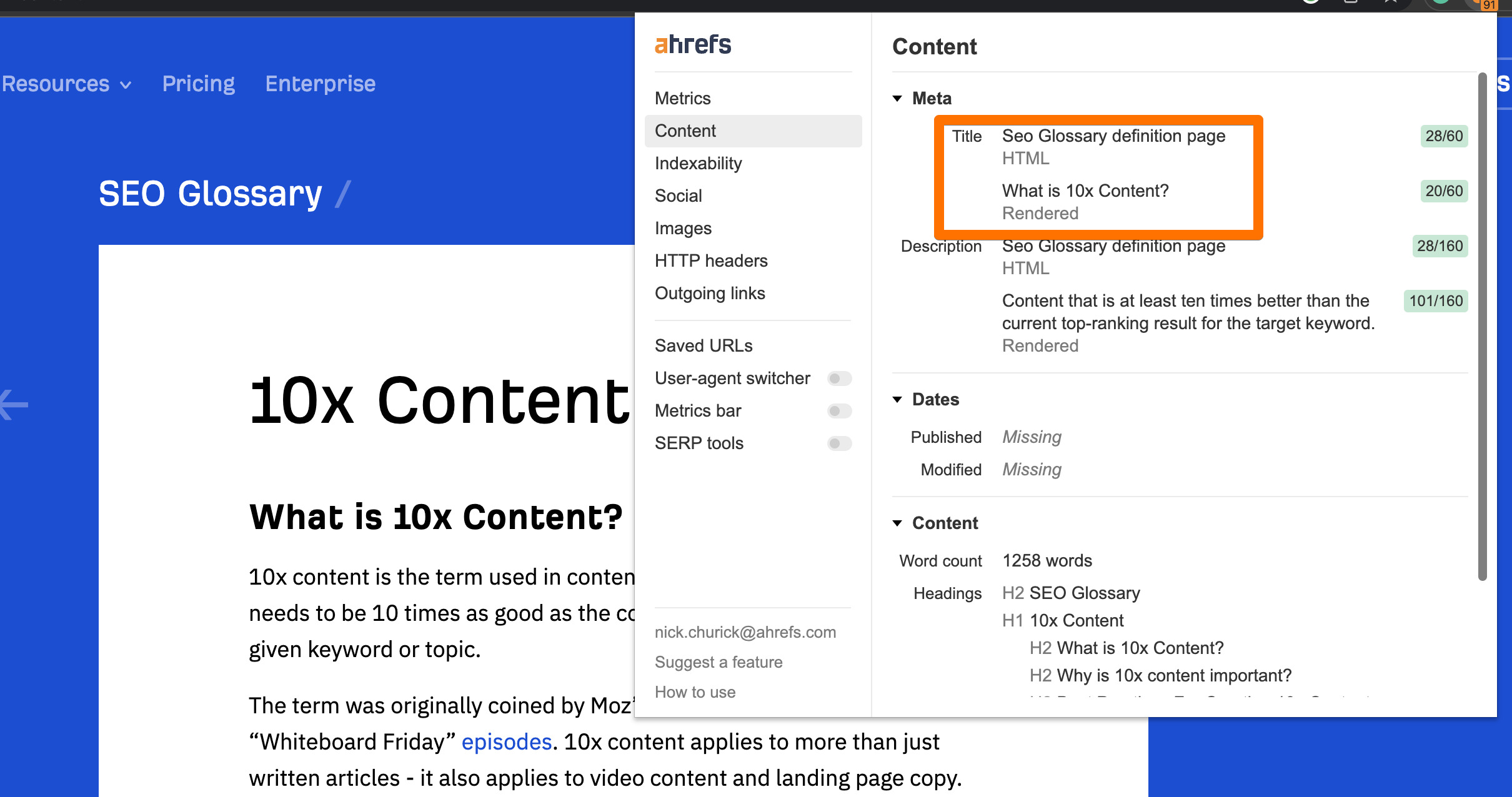
How do you find a title tag on the page?
You will find the title tag in the
section of the page's HTML code. But you should note that for JavaScript-powered pages, the "final" rendered title and the title in the source code aren't always the same.You can use our free SEO Toolbar that can check both:
What is the recommended length of a page title?
We recommend keeping your page titles between 50 to 60 characters because longer titles will be trimmed on Google’s SERPs.
The characters vary in pixel width, so there’s no exact character limit that will keep your titles under 600 pixels wide when shown on SERPs.