Nofollow
What is Nofollow?
Nofollow (rel=“nofollow”) is a link attribute that instructs search engine crawlers not to follow the link and thus not to crawl the linked page. The nofollow links do not influence the search engine rankings of the linked URL as Google does not transfer PageRank or any other signals across them.
The nofollow tag was originally introduced by Google in 2005 to combat link spam in comments.
In 2019 Google introduced rel=“sponsored” and rel=“ugc” attributes for sponsored and user-generated links specifically.
Here’s how it looks in the HTML code:
<a href="https://ahrefs.com" rel="nofollow">Ahrefs</a>
You should also note that if there’s a page-wide “nofollow” directive for crawlers in the robots meta tag or X-Robots-Tag, all links on this page automatically become nofollow.
<meta name="robots" content="nofollow">
Is “nofollow” important for SEO?
Nofollow links do not influence the search engine rankings of the destination URL.
However, some black-hat SEOs create nofollow links deliberately, trying to make their link profiles look more natural.
Also, you should understand that using the “nofollow” attribute on any form of paid links (sponsored posts, affiliate links, ads) can protect your website from penalties.
How to find nofollow links to your website?
You can easily identify nofollow links to any website with Ahrefs’ Site Explorer. Hear over to the Backlinks report and apply the “Nofollow” filter.
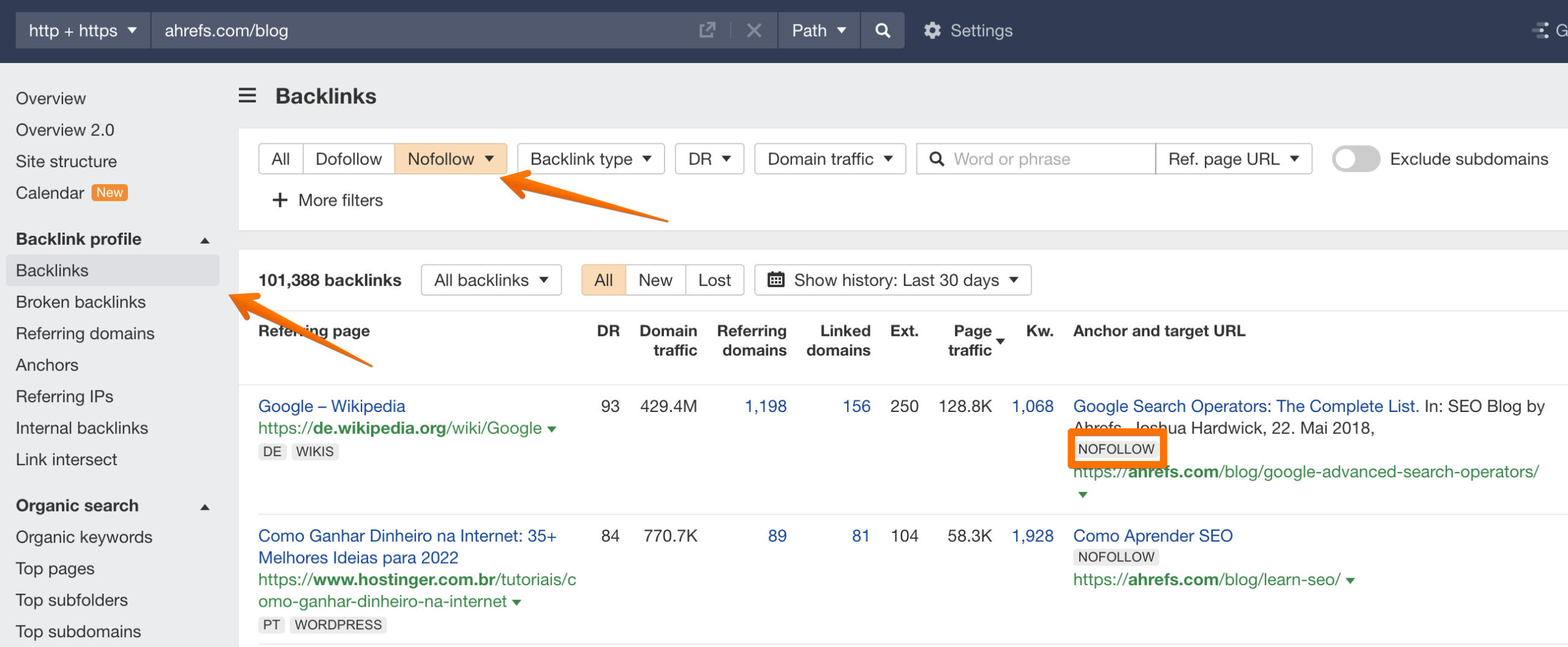
How to find nofollow links on your website?
To find all outgoing links on your website, you’ll need an SEO crawler.
You can use our free Ahrefs Webmaster Tools to analyze all pages on your website for nofollowed outgoing links (both internal and external).
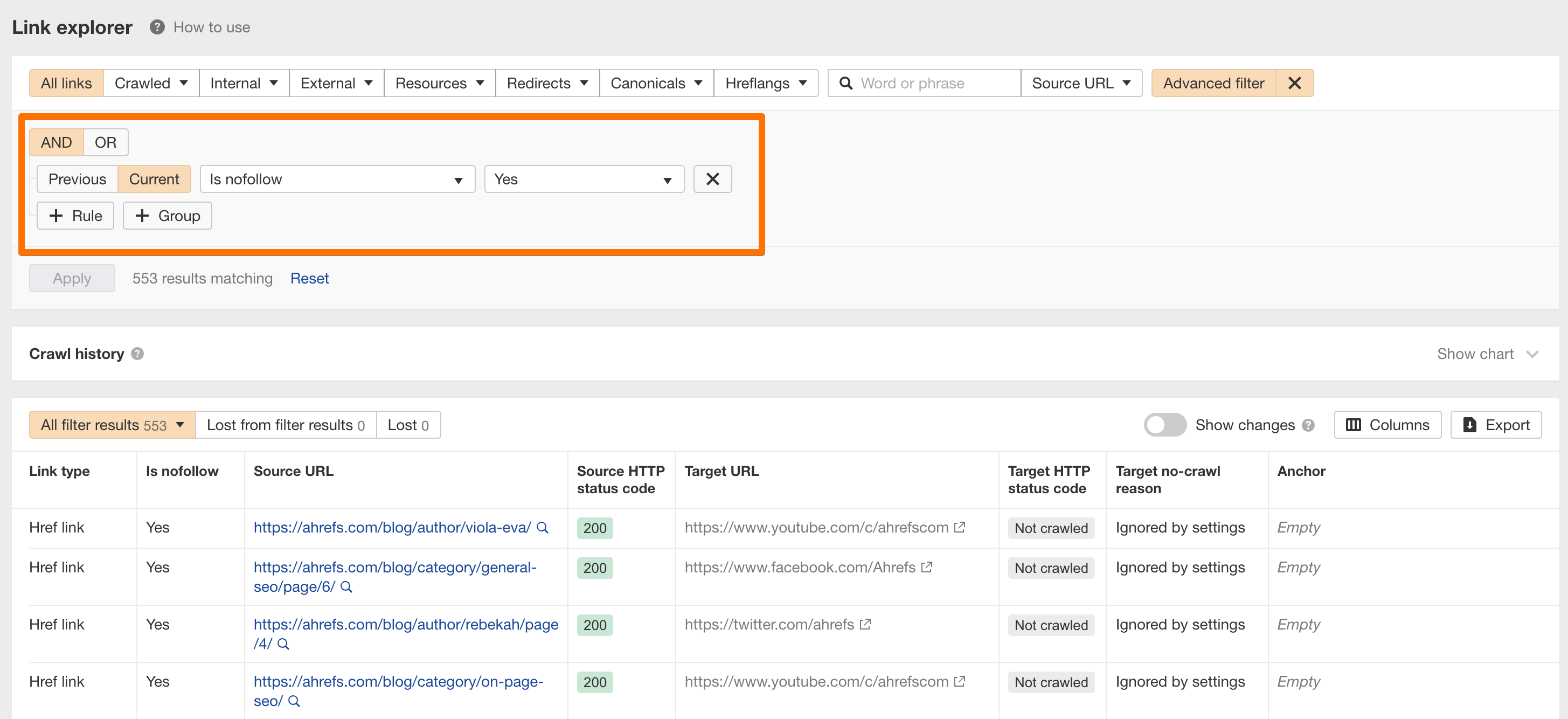
This audit will help you find potential issues or mistakes with the nofollow links on your website. For example, you should not “nofollow” internal links to the pages that you want to rank on Google.