H1 tag
What is H1 Tag?
The H1 tag (also known as a level-1 heading) is an HTML heading used to mark up the visible title of a web page.
Here’s how it looks in the page code:
<h1>59 Blogging Statistics for 2023</h1>
And here’s what it looks like on the page itself:
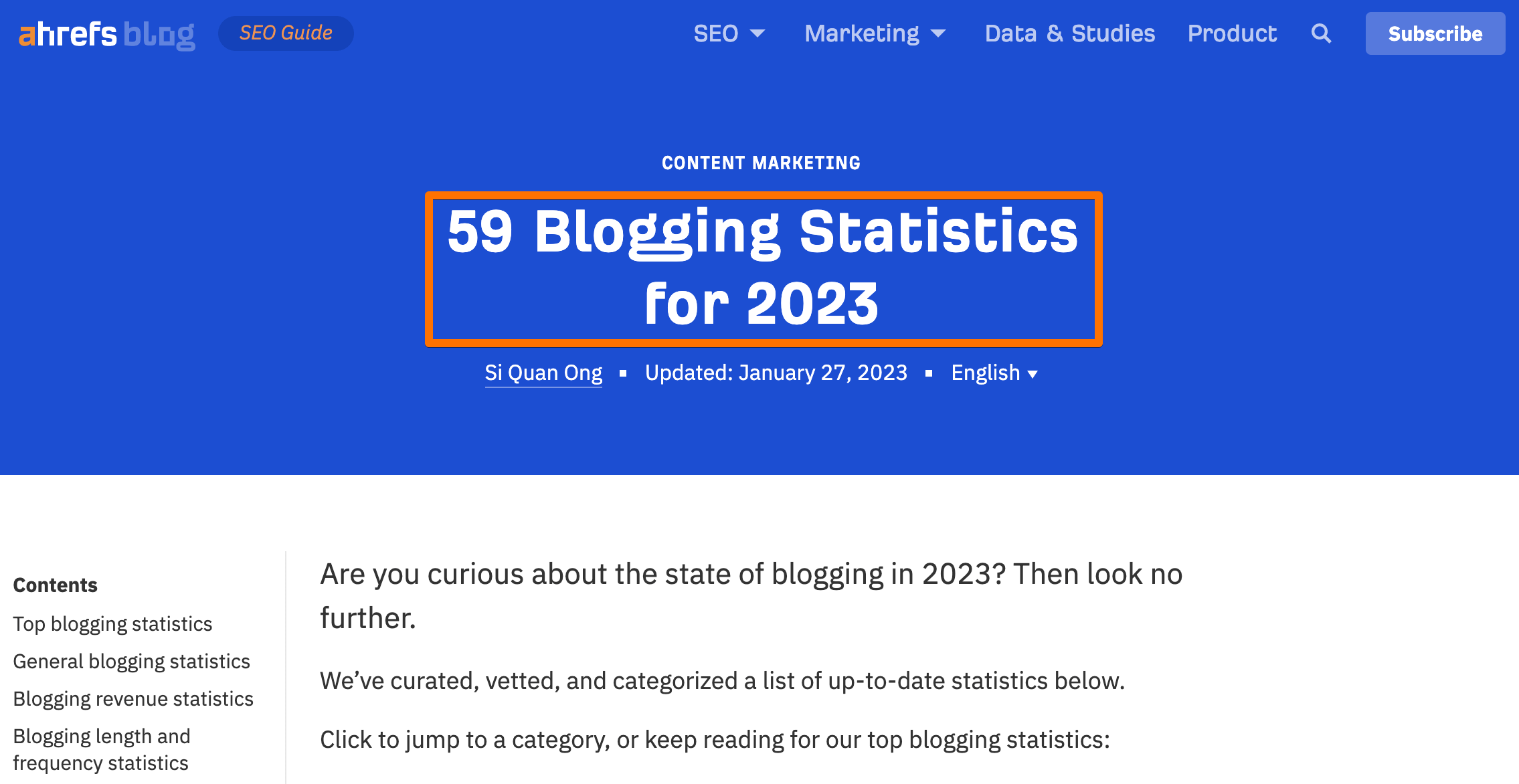
Although the H1 of a web page does not have to repeat the page title tag, you’ll often see that they’re using the same text. That’s because WordPress and a few other popular CMSs do that by default.
Why is the H1 tag important?
Here are two reasons why the H1 tag is important:
It helps search engines understand the content
Just like the page title and meta description, the H1 tag helps the search engines understand the page’s content. The more descriptive the H1 tag, the easier it becomes for Google to understand it.
…H1 elements are a great way to give more structure to a page so that users and search engines can understand which parts of a page are kind of under different headings. - John Mueller from Google.
It forms the first impression for the visitors
The H1 tag is the first visible element of the page for any visitor, and hence, it forms the first impression. It explains the page and gives the visitor a glimpse of the content. Thus, it can help the visitor become a reader.
SEO best practices for H1 tags
It is clear that the H1 tag helps the webpage from both – the humans’ and search engines’ perspectives. So, below are some of the best practices to follow for H1 tags from the SEO perspective.
1. Use one H1 tag per page
While John Mueller from Google suggests it’s okay to have multiple H1 tags on a page or no H1 at all, it is best to have one H1 per page. The H1 should be your main header for the page, followed by sub-headers H2s, H3s, and so on.
Google’s official documentation says:
Ensure that each page in your project includes a unique level-1 heading. In some publishing systems, a level-1 heading might be generated automatically based on a page title that you supply.
2. Include your target keyword
Along with the meta title, Google uses the H1 tag to determine the relevance of the content to a user’s search query. The H1 tag gives strong signals about the topic to Google. So, if the H1 is highly relevant to the search query, it can rank well for the same.
Including the main keyword or its close variant also helps the reader understand the topic of the page. However, you must include it only if it can be used naturally.
3. H1 does not have to repeat the title tag
The H1 tag should be similar to the page’s title so that users don’t feel deceived. However, it doesn’t need to be a replica of it. The title can be shorter (50-60 characters) to fit the SERP. But, the H1 can be longer to make it more elaborate or understandable to the readers.
4. Make sure every important page has an h1
Since H1 is the main heading, you must have an H1 on every important page of your website.
To find pages with missing or multiple H1’s, you can use our free Webmaster tools.
FAQs
Is it safe to have multiple H1 tags on a page?
Yes, it is absolutely safe to have multiple H1 tags on a page. However, it is best to stick to just one to make the heading structure more consistent.
What’s the difference between the H1 tag and the title tag?
The H1 and title tag are often mentioned interchangeably. While both act as page headings, they differ based on where they appear.
The title tag appears on search engine results pages (SERPs) and at the top of the web browser tab. However, it is not visible on the webpage. The H1 tag, on the other hand, appears on the web page.
How long should the h1 tag be?
Unlike the title tag, there’s no need to limit an H1 to fit into the SERP display. So it can be of any length, as long as it looks good on a page.