Canonical Tag
What is a Canonical Tag?
A canonical tag or rel=“canonical” is a snippet of HTML code that declares the canonical URL of the web page. In other words, it lets you define the main version for your duplicate, near-duplicate, and similar content under different URLs to instruct search engines on which version should be indexed.
Canonicalization helps you control your duplicate content by explicitly specifying to Google which URL is canonical and should be indexed.
Here’s what it looks like in the page code:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://ahrefs.com/blog/">
An alternative to canonical tags is implementing a rel=“canonical” HTTP header.
Why are canonical tags important?
Using the canonical tag is the primary way to solve duplicate content issues on a website. A canonical tag helps search engines find the most representative “canonical” version among the duplicate pages to indicate what needs to be indexed and re-crawled more frequently.
The tag also helps consolidate link signals from a set of duplicate pages to the canonical version (or the one you want to be ranked), thereby improving its overall ranking.
If you don’t use canonical tags on the duplicate pages of your site, Google will still attempt to identify the canonical page. However, there’s no guarantee that it will be the page version you want to be indexed.
Best practices for canonical tags
Here are a few things to keep in mind when using the canonical tags:
1. Always use the self-referential canonical tag
A self-referencing canonical tag references the URL of the given page, even if the page has no alternative versions. In this case, whenever a page is accessed via a URL with URL parameters, it will automatically point to the canonical version.
Although using self-referential canonical tags is not necessary, it is recommended.
“I recommend [using a] self-referential canonical because it really makes it clear to us which page you want to have indexed, or what the URL should be when it is indexed.
Even if you have one page, sometimes there are different variations of the URL that can pull that page up. For example, with parameters in the end, perhaps with upper lower case or www and non-www. All of these things can be kind of cleaned up with a rel canonical tag” - John Mueller from Google
2. Use absolute URLs
Absolute URLs (that contain all the information necessary to locate a resource) in canonical tags can help you avoid unintentional mistakes or misinterpretations of canonical URLs by search engines.
You can use relative URLs in canonical tags, but it’s recommended best SEO practice to use absolute URLs.
3. Don’t use the robots.txt file for canonicalization
The robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers where they can and can’t go on your site. If the URLs are disallowed in robots.txt, Google won’t read their canonical tags. Besides, link signals from these pages will not be consolidated.
4. Audit your website regularly
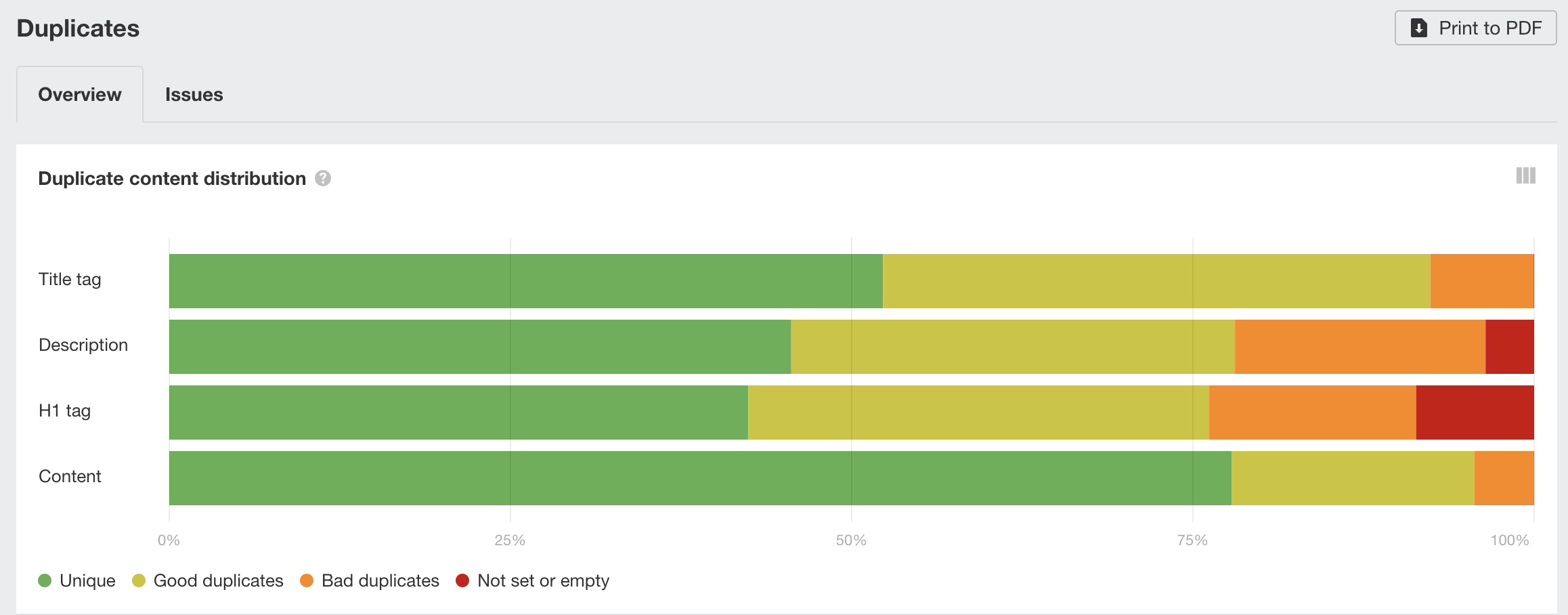
It’s important to monitor duplicate content issues on your website to ensure proper canonicalization of your pages.
Ahrefs Site Audit (or the free Ahrefs Webmaster Tools) can help you with that. You’ll be able to find the “duplicates” report that will show the duplicate and near-duplicate pages of your website that aren’t properly canonicalized.
FAQs
Is the canonical tag always necessary?
Although it is not necessary to use the canonical tag, we recommend using it. If there’s duplicate content without the canonical tag, Google may still try to find the canonical version. However, in the presence of a canonical tag, it would become clearer to the search engine.
What is a canonical URL?
A canonical URL is a URL of the preferred version of a page in a set of duplicate or near-duplicate pages. This URL is used in the canonical tag instructing the search engines about canonicalization.