Website Authority
What is Website Authority?
Website authority is an SEO concept that refers to the overall “strength” of a particular domain. Strength, in this case, is the ability (or likelihood) of a given domain to rank high in the SERPs and pass its backlink strength (“link juice”) to other websites.
The concept of website authority in SEO shouldn’t be confused with the Domain Authority (DA) as a metric. MOZ, a provider of SEO software, developed the latter to predict the likelihood of a given website appearing in SERPs and is measured on a scale from 1 to 100.
Ahrefs has its own proprietary authority metric, called Domain Rating (DR), used to estimate the site’s “link popularity” compared to other websites.
As a rule of thumb, a higher Domain Rating implies a more authoritative website.
Website authority is calculated based on different factors, depending on the specific tool used in the assessment. However, the most crucial is the website’s backlink profile - and, more specifically, the quality and quantity of the backlinks it receives.
Why is website authority important for SEO?
Google continues to insist that Domain Authority (as a metric) is not used as one of the factors for deciding how to rank sites in search engine results pages (SERPs). Then again, according to Google’s John Mueller, there is still a sitewide score that “maps to similar things.”
To understand website authority and its role in SERPs, we must first discuss how Google ranks sites and distinguish between “authority” as a metric and the concept of authority that a particular domain may have.
Google will consider more than 200 factors before showing results for a particular search query.
Some of the most important include the content of the page and its backlink profile - along with specific technical aspects, like mobile-friendliness and speed.
Here at Ahrefs, we explored the connection between keyword rankings and Domain Rating. After examining 218,713 domains (each ranking for at least 100 keywords), the study has concluded there’s a clear correlation.
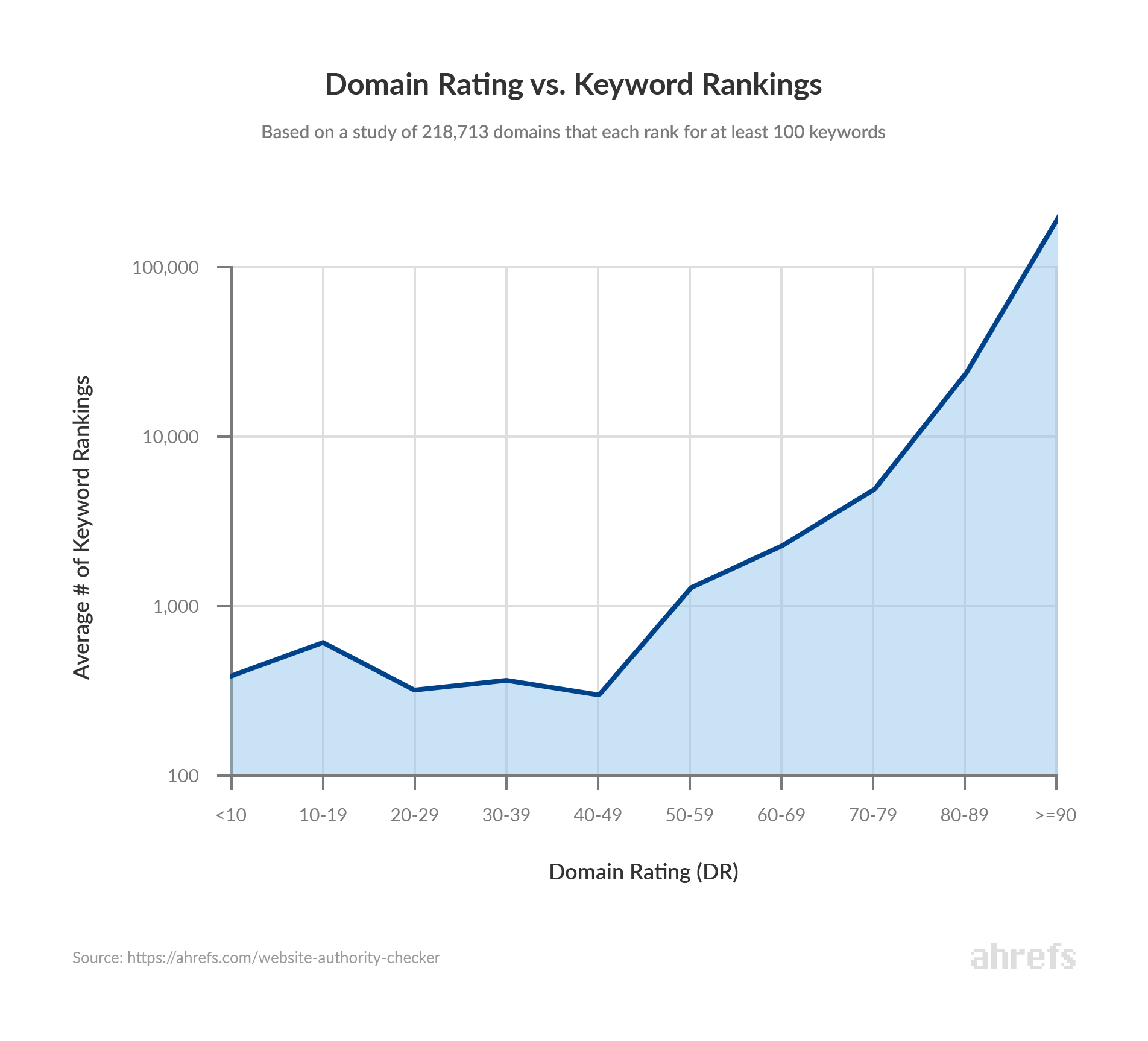
After all, it’s confirmed that PageRank is still used as a ranking signal in Google’s algorithm.
And while you shouldn’t focus on a single metric because it doesn’t paint the real picture of your website’s performance or measure the success of a link-building campaign, Domain Rating can still be used to:
- Compare your website to other websites in the world
- Compare your website to other websites in your niche
- Estimate the “value” of a backlink when vetting link prospects
- Estimate a website’s ability to get organic traffic
How to increase the website authority?
Building website authority should be a long-term strategy; don’t expect instant, overnight results. Instead, tackle specific points of optimization - and monitor your site’s performance. Additionally, when building up your website authority, consider the following:
1. Don’t rely on authority metrics blindly
If you’re working on link-building, focusing solely on Domain Authority (or Domain Rating) score would be a mistake. Earning a backlink from a website with a high DR score does not guarantee the quality of the said link.
Instead, when estimating the “value” of a backlink, it is essential to consider other factors, like:
- The number of pages on the referring website
- The amount of organic traffic the website is getting
- The number of other websites that site is already linking to
- How relevant the referring website is to your topic
- The website’s quality (design, optimization, content, etc.)
Unless all these other variables are satisfactory, even a link from a website with DR75 or more won’t improve your website’s authority.
2. Don’t be afraid to get links from sites with low authority metrics
Earning high-quality, relevant backlinks should be an integral part of your strategy if your goal is to get traffic from search. A strong backlink profile (both in terms of size and quality) is crucial for showing Google that your site’s worthy of ranking higher.
Generally speaking, Google would prefer if these backlinks came from high-authority sites, which would boost your own site’s authority.
Still, that doesn’t necessarily mean that getting backlinks from sites with a lower DR wouldn’t do you any good. You shouldn’t judge the quality of a website based on a single metric - especially if it’s highly relevant to your page’s topic.
Website authority is good - but relevance is paramount.
If you use Content Explorer, you will see there are thousands of low-DR websites getting lots of organic traffic from Google.
3. Don’t inflate your authority metrics
You would imagine that websites with higher website authority would dominate the SERPs - and you wouldn’t be alone in that assumption. Many (especially those new to SEO) do believe that a higher DR guarantees a better ranking.
But it’s not that uncommon for pages from lower authority websites to rank higher than websites with more authority. Why?
Because the DR score isn’t an indicator of quality content.
Unfortunately, many will still try to manipulate these metrics and boost them artificially through a PBN or link farms. If the thought ever crossed your mind, just know that Google will recognize it, which can lead to penalties.
The main takeaway is that website authority scores mean nothing without quality content, no matter how impressive.
Instead of focusing on finding ways to boost your site’s DR artificially - mainly through black-hat SEO tactics - turn your attention to producing content that adds actual value and is of interest to your audience.
FAQs
Does Google use website authority as a ranking factor?
According to Google representatives, Domain Authority (metric) is not used as a ranking factor.
With that said, the chances are that Google is using a similar internal metric to measure the authority of a particular website based on several factors, including the quality and strength of its backlink profile.
What website authority is good?
There is no straightforward - let alone universal - answer to this question; the same may be said for most other SEO concepts.
For instance, a small or recently launched business will have a low DR score - but with high-quality content that targets long-tail keywords, it could still rank high, provided that SERP competition is low.
How is website authority calculated?
The authority metric developed by Ahrefs, Domain Rating, is displayed on a 100-point scale and calculated using factors such as:
- The number of domains linking to the target website
- The Domain Rating of the referring domains
- The more websites the referring domain links to, the less DR it passes to these sites