Subdomain
What is a Subdomain?
A subdomain is a part of a website that’s placed under that website’s root directory. It is represented by an addition at the front of the root domain name.
In app.ahrefs.com, app is a subdomain of the root domain ahrefs.
Having subdomains is helpful for keeping a website organized.
Another way to create sections within a website’s structure is with subdirectories. These are also known as subfolders, as they exist within folders under the root directory.
It’s easy to visually distinguish subdirectories from subdomains, as subdirectories are placed behind the root domain name.
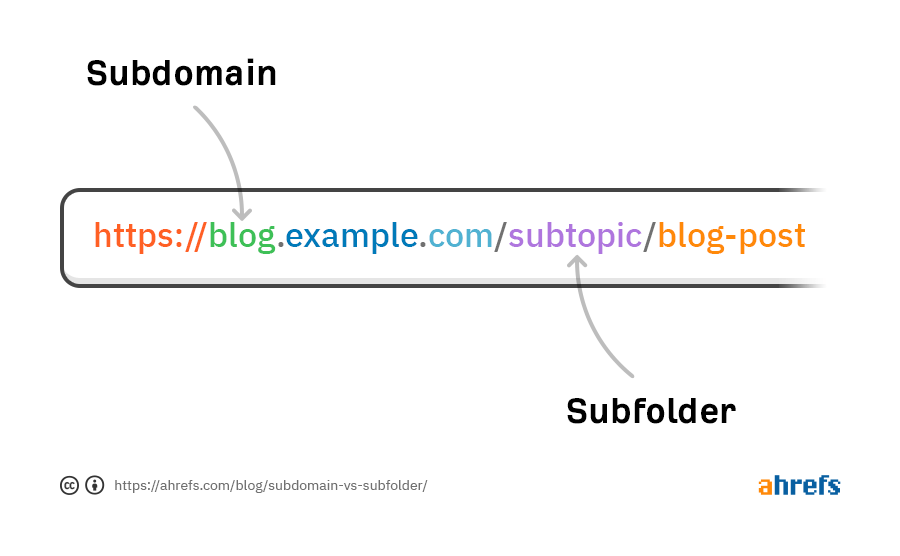
Both subdomains and subdirectories are part of the main website, and both can go multiple levels down. However, it’s more common to see nested subfolders than multiple levels of subdomains.
For subdomains, these can look like:
- uk.store.website.com
- de.store.website.com
- fr.store.website.com
For subfolders, these can look like:
- website.com/blog/marketing
- website.com/blog/sales
- website.com/blog/seo
Technically speaking, the www in URLs is also a subdomain, but it’s not used in the way that subdomains are generally used.
The www subdomain dates back to the time before the World Wide Web became popular to indicate that a URL was a website address. Nowadays, it’s become largely redundant.
Are subdomains important for SEO?
Using subdomains or subfolders doesn’t make any difference to Google. This is a highly debated topic in the SEO community, but Google has repeatedly made clear that both are fine.
John Mueller dedicated a video to this in 2017.
He confirmed this stance a year later in response to some SEOs who wouldn’t accept it:
What reason could Google possibly have to be misleading here? “We’re running low on subdirectory-servers”? I knew this would trigger some folks, so I spent time to prod folks internally about the reality, and there’s nothing to hide here.
— 🐐 John 🐐 (@JohnMu) January 24, 2018
One of the reasons that some SEOs keep advocating for the use of subfolders over subdomains is because of the many case studies that “prove” subfolders are better. The problem with these studies is that they don’t isolate the effects of just the migration from the subdomain to the subdirectory.
During the tracked periods of these studies, other changes took place as well. The internal linking structure of a website improved, or more content was added.
So what should you take into account when deciding whether to use a subdomain for a section of your website? Let’s have a look at the benefits and downsides of subdomains.
Benefits of subdomains
The first benefit of subdomains is they’re great for staging purposes. Having all of the URLs on your staging site on a subdomain, such as staging.website.com, makes it easy to keep track of things.
If you don’t link your staging subdomain to your main domain, users likely won’t find it. You can always password protect it as well.
However, you still need to disallow crawling of the staging site in the subdomain’s robots.txt file, as well as noindex it.
Subdomains are also great for managing website sections with different purposes.
While your main site runs on WordPress, your knowledge center and store can easily run on their own platforms if they’re subdomains. And when you have a SaaS business, you can use something like app.website.com structure for your tool.
Lastly, subdomains can help you maintain a simpler URL structure. Say your business targets an international audience and uses subdirectories to categorize the content on your site. In that case, you may want to use subdomains for the international versions of your site.
It’s cleaner to have something like…
- uk.website.com/category/
- es.website.com/category/
than
- website.com/uk/category/
- website.com/es/category/
Downsides of subdomains
Subdomains may be a bit more complicated to set up than subfolders. This means they’re also more prone to errors. You’ll want to double-check your setup, any internal links you build within or to your subdomains, as well as whether you’re tracking your subdomains correctly.
You may also need to obtain an additional TLS/SSL certificate for a subdomain (unless you already have a Wildcard certificate).
Another downside is that it takes Google a little longer to learn how to crawl your site when you have one or more subdomains. But according to John Mueller, this process just spans a matter of days.
In the end, the choice is a personal one. Google doesn’t prefer subdirectories over subdomains.
Best practices for subdomains
1. Make sure that subdomains have their own robots.txt file
Google looks at robots.txt files per hostname, which means that it won’t consider instructions for your subdomain in the robots.txt file for your main domain. Each subdomain should have its own robots.txt file.
2. Provide internal links between subdomains and the main domain
By interlinking your subdomain(s) and your main domain, you make it clear to Google that these are all part of the same website. It also makes it easier for the search engines to crawl all of the pages on your site and for PageRank to flow between those pages.
Lastly, interlinking your subdomains and main domain is key to creating easy navigation for the users of your site.
3. You may need to add a subdomain to Google Search Console
If your website was added to Google Search Console (GSC) as a URL-prefix property, such as https://www.example.com/ or https://example.com/, then GSC won’t track https://blog.example.com/ by default.
You’ll need to either add a new URL-prefix property for https://blog.example.com/ or add example.com as a domain to include everything.
FAQs
Are subdomains better than subfolders for SEO?
No, they’re equally good. Google has confirmed this.
Are subdomains different websites?
If you incorporate a subdomain as a part of your main website and connect the two through internal linking, Google will likely treat your subdomain the same way it will a subfolder.
However, if you’re not treating your subdomains as part of your main website (meaning, if you don’t create any internal links between your subdomains and your main website), then Google may treat them as separate sites.
Are backlinks from the main domain better than the links from the subdomain?
If all other factors (such as link relevance, PageRank, etc.) are the same, there is no difference between a link from the main domain and a link from a subdomain.