Sitemaps
What is a sitemap?
A sitemap is an XML file listing all the pages on your website that you want search engines like Google to index. It can also include other information, such as the date each URL was last modified.
Why are sitemaps important?
Sitemaps are important because they help Google and other search engines discover the pages on your website. If search engines can’t find your pages, they can’t index them. And if they can’t index them, you can’t rank in the search results.
Best practices for sitemaps
Let’s take a look at a few best practices to help you create and submit a sitemap.
1. Create a sitemap
Sitemaps aren’t the only way that search engines like Google discover pages on a website. They also crawl the web, where they “follow” internal and external links on known pages to find more pages.
However, having a sitemap is still best practice for all website owners because it can:
- Help search engines to discover your pages faster.
- Give search engines a more complete view of your website (as some pages may not have backlinks or internal links).
- Tell search engines which pages are important to you.
That last point is particularly important because, in some cases, a sitemap can help prevent undesirable pages from appearing in the search results over desirable pages. This is because Google uses sitemaps as a canonicalization signal.
Follow the tutorial below to create a sitemap if you don’t already have one.
Recommended reading: How to Create an XML Sitemap
2. Make sure you didn’t exclude important pages
Most sitemap creation tools and plugins exclude noindexed pages. This makes sense because the search engines can’t index “noindexed” pages, so they don’t really need to know about them.
Unfortunately, it’s easy to accidentally noindex important pages and exclude them from search.
To ensure you don’t have this problem on your website, use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT) to check for rogue noindex directives:
- Sign up for a free AWT account.
- Follow the instructions to add and verify your website, making sure to leave the option for a site crawl checked.
- Go to Site Audit. Wait for the crawl to finish if it hasn’t done so already.
- Click on your project.
- On the left menu, click All Issues.
- Click the ‘Noindex page’ warning. (If it isn’t there, Site Audit didn’t discover any noindexed URLs).
- Click “View affected URLs.”
- Make sure that all of the noindexed pages should indeed be excluded from indexing.
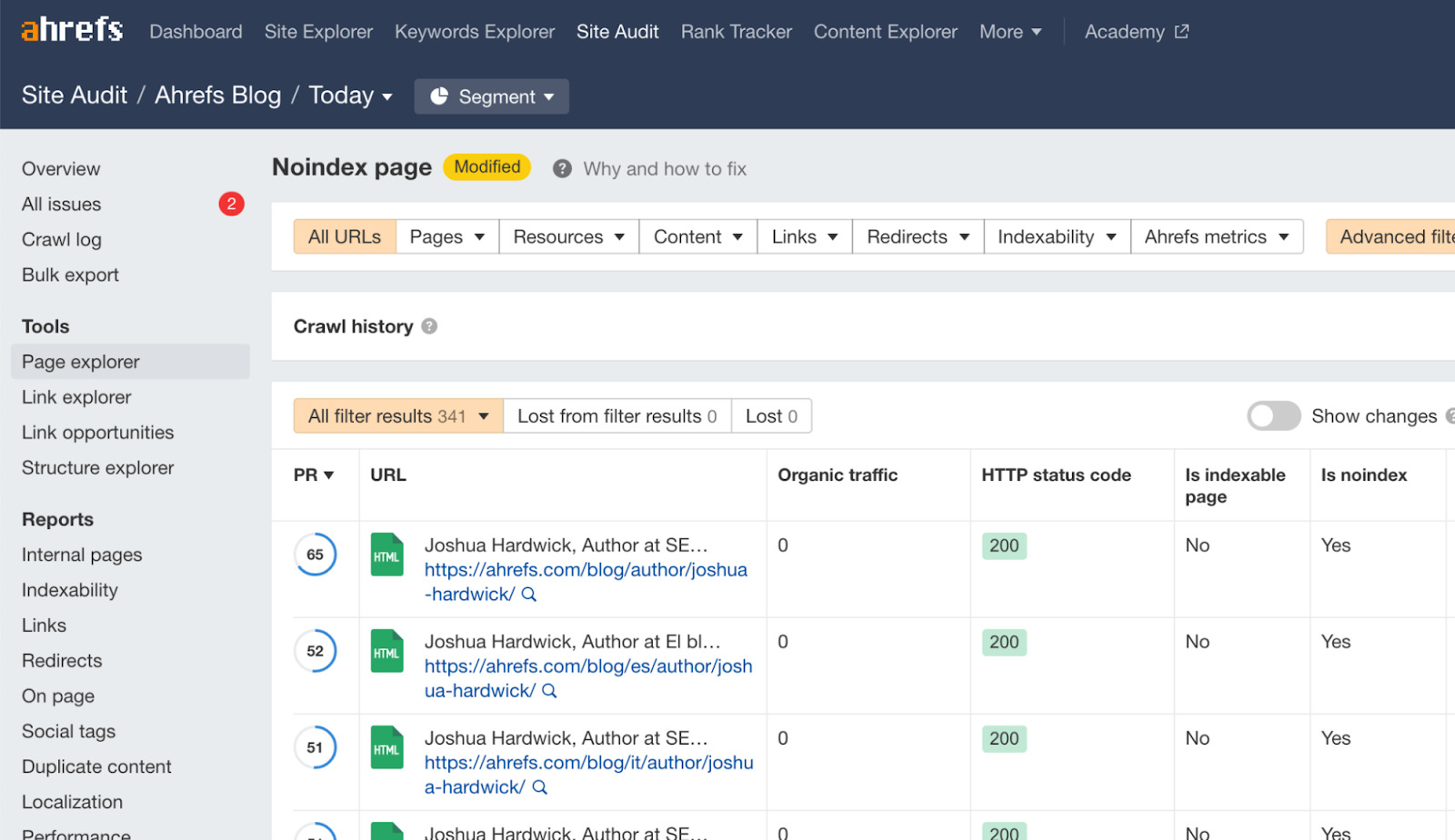
If you spot accidentally noindexed pages, remove the noindex directive from them and add them to your sitemap. (This will happen automatically if you’re using a popular plugin like Yoast to create and manage your sitemap.)
3. Submit your sitemap to search engines
Search engines like Google won’t know about your sitemap unless you tell them about it. How you do this depends on the search engine.
Here’s the process for submitting your sitemap to Google:
- Sign in to Google Search Console.
- Select your property.
- On the left menu, click Sitemaps.
- Enter your sitemap URL.
- Click submit.
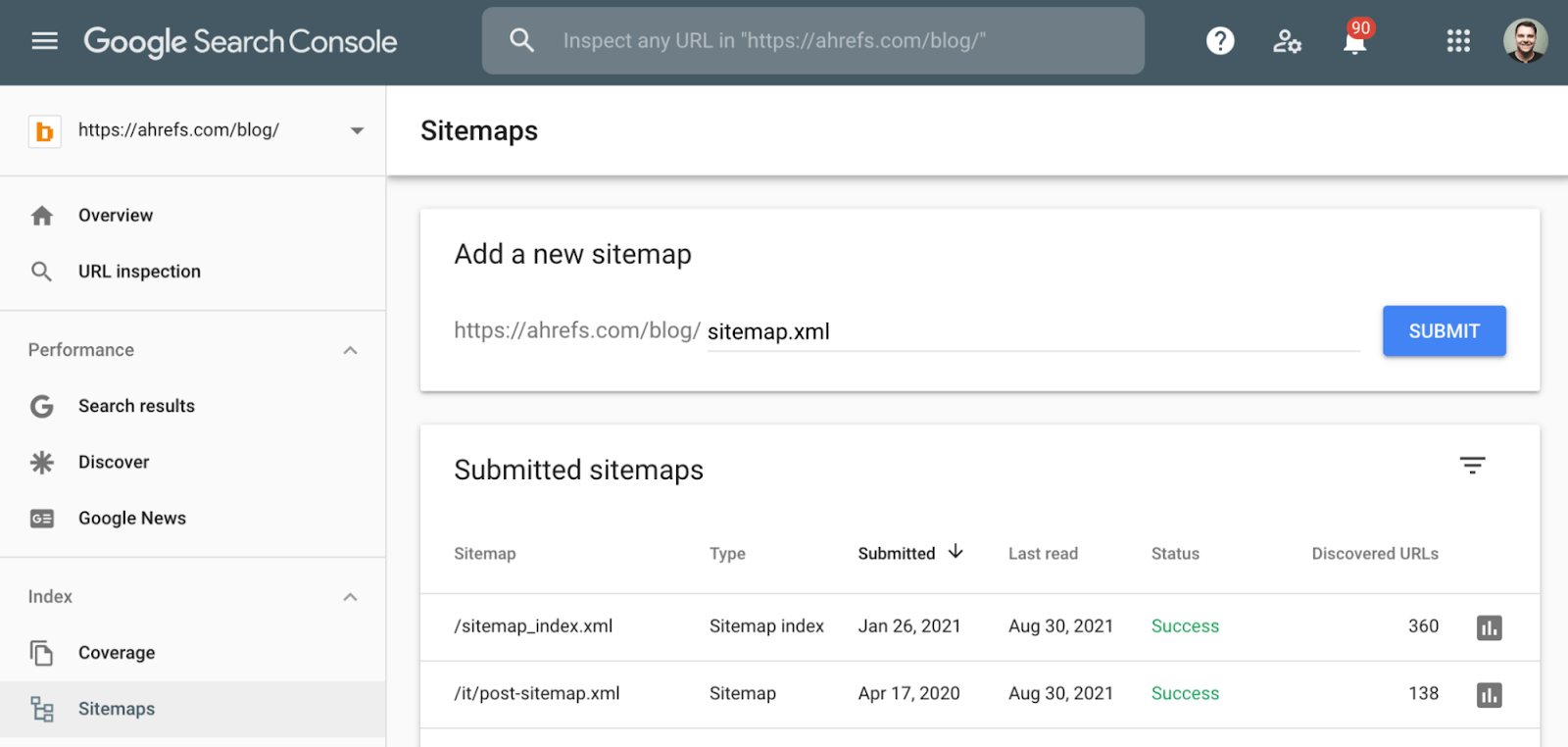
Provided that you keep your sitemap up to date, you only need to submit it to Google once. Google will revisit your sitemap periodically to find new pages.
Most other content management systems like WordPress and Wix add and remove pages from your sitemap for you as you make changes to your website. So if you’re using one of these, it’s pretty hands-off once you submit the sitemap.
Follow the tutorial below for instructions on how to submit to Bing and other search engines:
Recommended reading: How to Submit Your Website to Search Engines
FAQs
How do I find my sitemap?
If your website has a sitemap, you can usually find it at one of these URLs:
domain.com/sitemap.xml
domain.com/sitemap_index.xml
How do I add my sitemap to robots.txt?
You can add your sitemap to your robots.txt file by adding this line:
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/my-sitemap.xml
Where do I put my sitemap?
Google recommends putting your sitemap in the root directory of your website so it can affect all pages on the website.