Hreflang
What is Hreflang?
Hreflang is an HTML attribute that informs search engines about the multiple versions of a page for different languages or regions.
It helps Google to serve the correct localized version to the searchers.
There are three ways to apply the hreflang attribute:
- HTML tags
- HTTP headers
- Sitemaps
Here’s how hreflang is implemented in the HTML code of our blog homepage:
<link rel="alternate" href="https://ahrefs.com/blog/" hreflang="x-default">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://ahrefs.com/blog/" hreflang="en">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://ahrefs.com/blog/zh/" hreflang="zh-Hans">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://ahrefs.com/blog/ru/" hreflang="ru">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://ahrefs.com/blog/de/" hreflang="de">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://ahrefs.com/blog/es/" hreflang="es">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://ahrefs.com/blog/it/" hreflang="it">
Why is hreflang important for SEO?
Hreflang is important for SEO because it helps search engines discover and serve the relevant localized version of your pages based on the user’s language and/or region.
It’s one of the crucial components of international SEO while expanding your online presence in multiple countries.
Moreover, the group of hreflang pages shares each other’s ranking signals.
According to the explanation from Google’s Gary Illyes, the page that is the best match will determine the ranking position, but the most relevant page for a user will be shown in the SERPs.
Thus, hreflang tags can impact your rankings directly.
Besides, hreflang is also one of the effective ways to resolve duplicate content issues on your site. Let’s say you’re targeting the audience in the US and UK with two different versions of the same page.
Apart from minor differences like some spellings, currencies, etc., the rest of the content on both pages will be identical. So you need to signal Google about two different versions with hreflang.
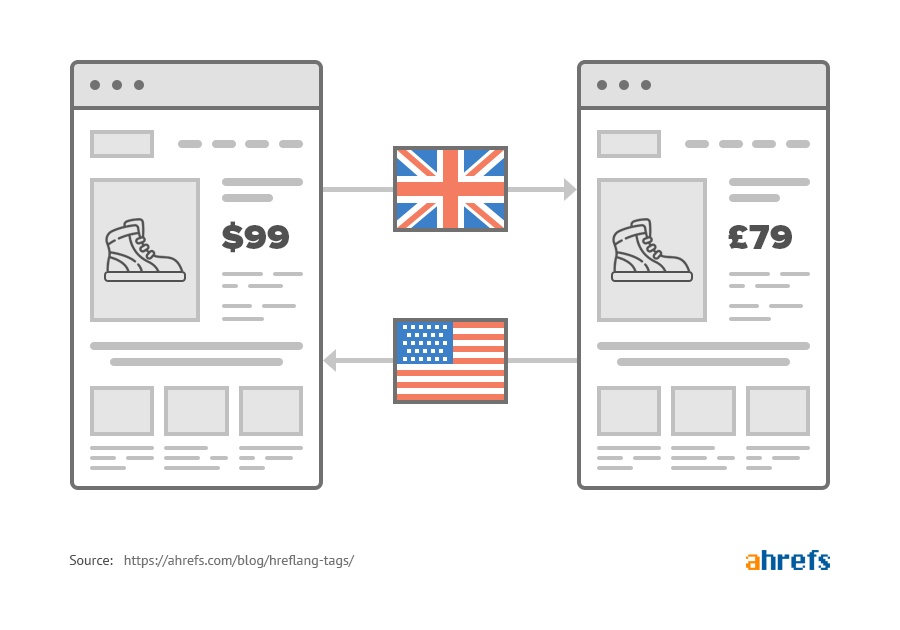
Without the hreflang attribute, Google may see these pages as duplicates and index only one of them. As a result, the other page wouldn’t get visibility and traffic.
Hreflang best practices
Now, let’s understand some best practices to implement hreflang tags correctly.
1. Always use self-referencing hreflang tag
Whenever you apply hreflang tags on a page, ensure that you’ve added a self-referencing hreflang link to that page.
For example, your site has the following English and Italian versions of a page:
https://example.com/hello and https://example.com/ciao
In addition to
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="it" href="https://example.com/ciao" />
the English version must also refencence itself
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://example.com/hello" />
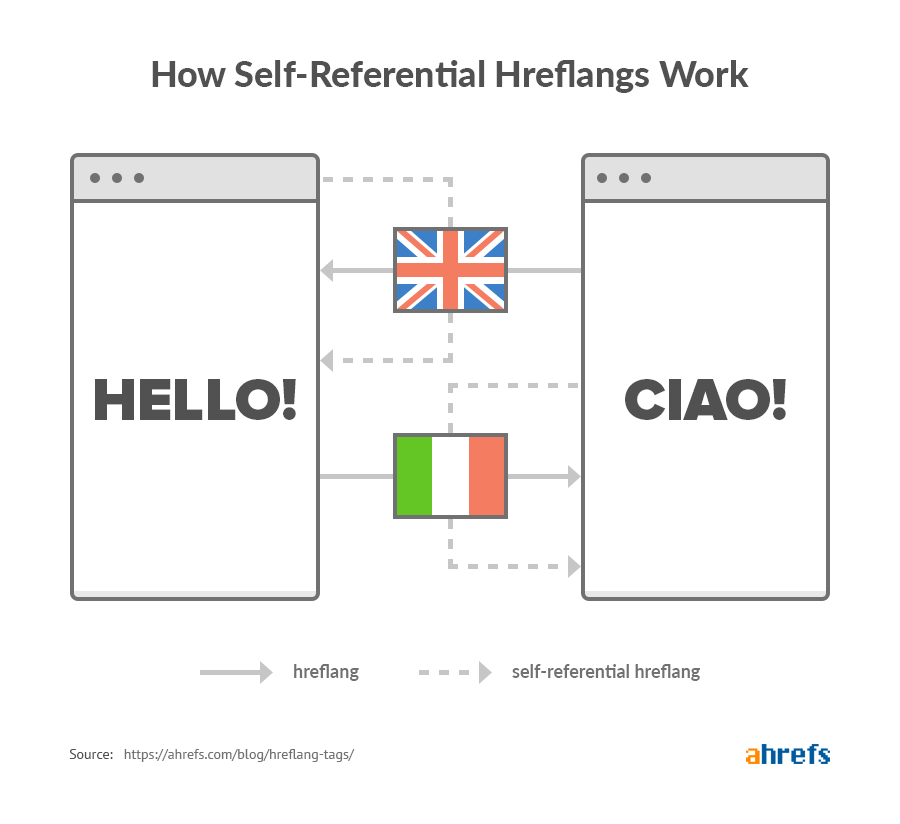
Although some SEOs argue that it’s an optional practice, Google’s guidelines say it’s a must.
2. Make sure the language and region codes are valid
Googlebot identifies the value of the hreflang attribute with the help of language and region codes. Google-approved format for language code is ISO 639-1 and ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 for region code.
While the language code is mandatory, the region code is optional in the hreflang attribute. So, if you’ve specified only one code, Google considers it language code by default. Hence, you must use the correct format for codes.
For example, if you’re targeting the UK, the language-location code must be en-gb, not en-uk.
3. Add “x-default” tag for unmatched languages
The hreflang x-default tag tells Google that the page is for every other language that is not specified in the hreflang section.
Simply put, it acts as a fallback page to be shown to users that don’t match the specified language codes. It’s not a mandatory practice, but Google recommends it.
It looks like this:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://example.com/" />
4. The set of hreflang tags must be identical on all page versions
The easiest way to ensure the accuracy of hreflang tags is to check whether tags are identical across all page versions.
In other words, every page in the group must have the exact same set of hreflang links.
Getting back to our blog homepage example, it has six language versions, and each localized version has the exact same set of 7 hreflang links (6 languages + x-default).
FAQs
How to generate hreflang tags?
Although everyone can write the hreflang tag manually, there are tools like Hreflang Tags Generator that help you generate it automatically. You can just fill in the details, and it’ll provide you with the correct hreflang tags for your pages.
How to find hreflang issues?
If you want to find the hreflang issues for individual pages, you can use the Hreflang Tags Testing Tool. But if you want to check the hreflang issues for your entire site, it’s better to use Ahrefs Site Audit. It’ll crawl all the pages on your site, highlight all the issues (including hreflang issues), and provide detailed reports.