Crawl Budget
What is Crawl Budget?
The crawl budget is the amount of time and resources a search engine assigns for crawling a particular website. In other words, it is the maximum number of pages a search engine can crawl on your site within a specific timeframe.
The crawl budget can vary for different search engines (or crawlers).
Google states that you shouldn’t worry about the crawl budget unless:
- Your site has 1 million+ unique pages with content that changes around once a week
- You have a medium-sized website i.e., around 10k pages, and change content frequently (daily)
- You run a news website
- Search Console classifies the majority of your site’s URLs as Discovered - currently not indexed.
Each website gets a different crawl budget based on these two factors:
- Crawl demand. The number of pages, posting/updating frequency, and popularity of the pages define it.
- Crawl rate limit. It is impacted by server capabilities, crawl limit set (in Search Console) by the site owner, the search engine’s crawling limit, etc. Google may also auto-adjust the crawl rate when the server is slow and vice versa.
Why is the crawl budget important?
The crawl budget is important because it affects how many pages Googlebot can crawl on your site. Besides, it also influences how often Googlebot can recrawl your web pages to update its index.
Google has enormous resources, yet it cannot crawl (and regularly recrawl) all pages of the Internet. As a result, Google allocates a crawl budget to websites.
And that’s why you want to ensure that your crawl budget is not being wasted on crawling the unimportant pages of your site.
That said, you need not be bothered about the crawl budget if you’re running a standard blog or small website.
How to increase the crawl budget?
Here’s how you can optimize your site’s crawl budget.
1. Speed up your server and decrease page loading times
The server response time and page loading speed directly affect crawling. It works something like this:
When Googlebot crawls your site, it downloads the resources first and then processes them. If your server responds quickly to the crawl requests by Google, it can crawl more pages on your website.
So, use a fast and reliable web hosting service and Content Delivery Network (CDN) to improve server initial response time.
At the same time, decrease your page loading times by:
- Preventing crawling of large but non-critical resources using robots.txt
- Avoiding long redirect chains
- Getting rid of heavy and poorly-coded themes and plugins to reduce page bloat
2. Add more links
The number of links to a page tells Google about the importance of this page. Googlebot prioritizes crawling pages with more backlinks and internal links.
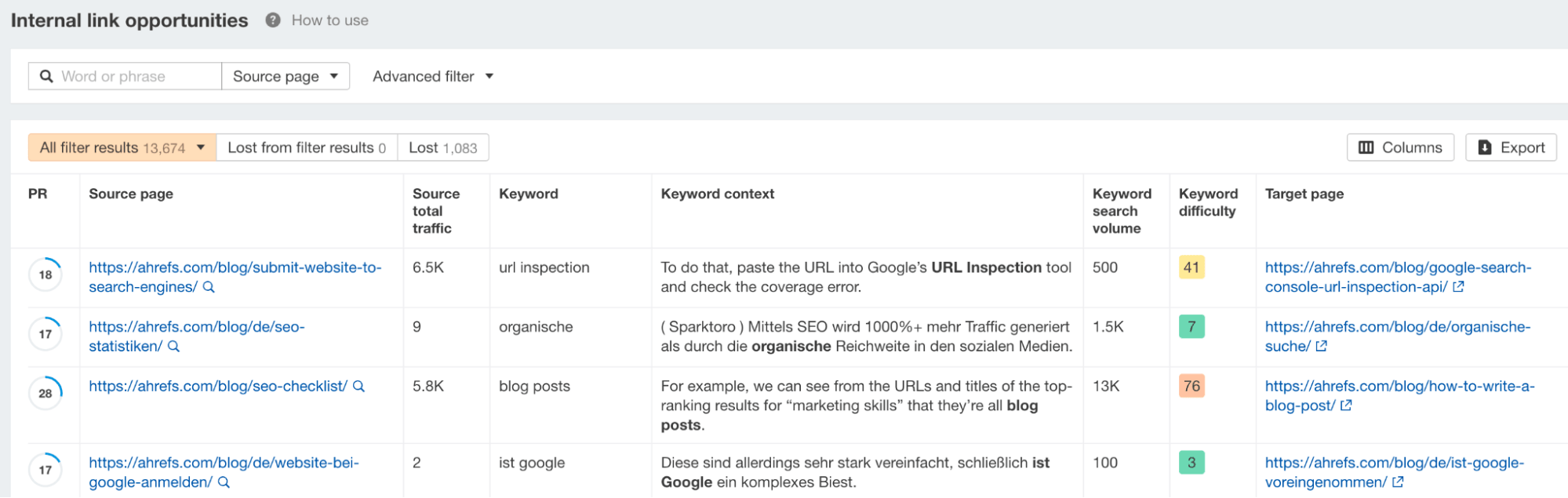
So, you can increase your crawl budget by adding more external and internal links to your pages. While getting backlinks from external sites may take time and is not (completely) in your control, you can start with the easier option—internal linking.
You can get internal linking suggestions by auditing your website with our Site Audit tool.
3. Fix broken links and decrease redirects
Too many broken internal links (404 or 410 response codes) and redirected URLs (3xx) can waste your site’s crawl budget. Although these pages will have low crawl priority if they’ve remained unchanged for a while, it’s better to fix them to optimize your crawl budget and for overall site maintenance.
You can easily find the broken, and redirecting URLs on your site in the Internal pages report in Site Audit or using our free Webmaster Tools.
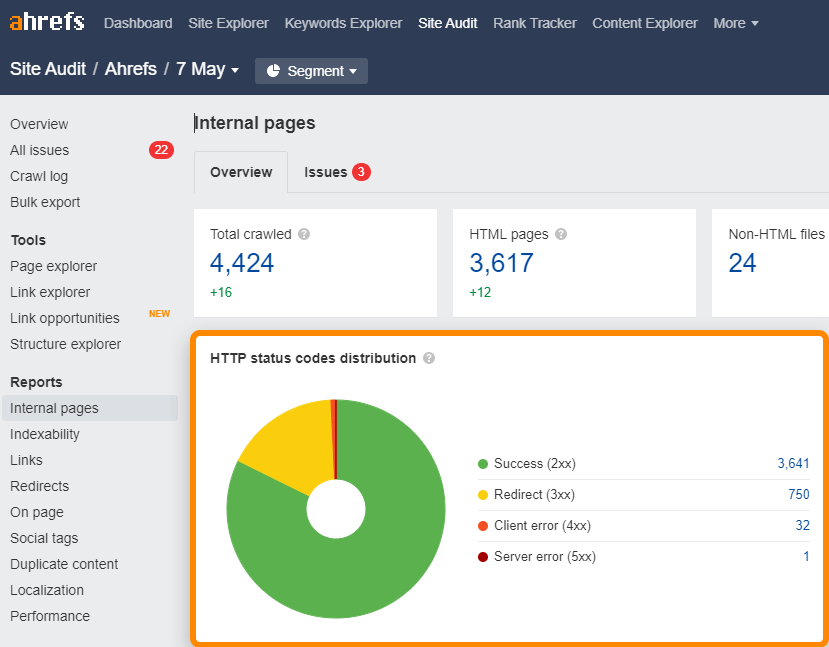
Once you find the broken internal links, you can reinstate the page at the same URL or redirect the URL to another relevant page.
For the redirects, see if there are many unnecessary redirects and redirect chains and replace them with a direct link.
4. Use the Indexing API if possible
Another way to get your pages crawled faster is by using Google’s Indexing API. It lets you notify Google directly whenever you add, remove, or update pages on your site.
However, the Indexing API is currently available only for use cases like live videos and job postings. So if it’s applicable to your site, you can use it to keep your URLs updated in Google’s index and search results.
FAQs
Does Googlebot respect the crawl-delay in robots.txt?
No, Googlebot doesn’t respect the crawl-delay settings applied in a robots.txt file.
When should you care about the crawl budget?
You should care about the crawl budget only if you’re operating a very large site i.e. more than 1 million pages or a medium-sized website with very frequent (daily) changes in content. That said, most of the sites don’t need to worry about the crawl budget.
How can I check the crawl budget for my website?
You won’t find the exact number for crawl budget anywhere. But you can check the overview of Google crawl activity in the Crawl Stats report in Google Search Console.